Sample Questions
1 of 20
Which of the following is the most correct statement based upon imaging:
2 of 20
A4C cine image is shown below
Findings are consistent with which of the following
3 of 20
PLAX M Mode is shown below. Cursor line is placed through the aortic valve. Findings are consistent with
4 of 20
Severe AR is indicated by which of the following:
5 of 20
Calculation of Effective Regurgitant Orifice Area (EROA) by the PISA method is an example of
6 of 20
Aortic regurgitant volume calculation by flow convergence (PISA method) uses which of the following equations:
7 of 20
Suprasternal image is shown below. Combined colour Doppler and M mode of flow in the descending aorta is shown. Findings are consistent with
8 of 20
Aortic valve dimensionless index is defined by which of the following
9 of 20
Incorrect measurement of LVOT diameter resulting in underestimated LVOT diameter will have which effect on subsequent estimation of AS severity
10 of 20
Estimation of mitral regurgitation severity is affected by severe aortic stenosis in which way
11 of 20
Echo data are shown below. If LVEF is 35% and BSA (body surface area) is 1.8m², findings are consistent with which of the following: 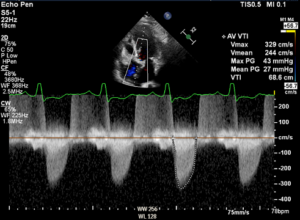
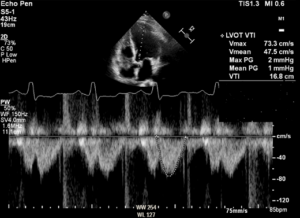
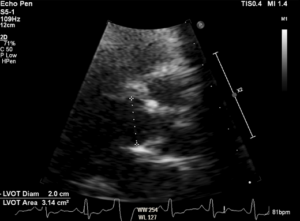
12 of 20
Which mitral valve scallops are visible in A2C
13 of 20
Waveform from CW Doppler interrogation of mitral valve inflow is shown below. Findings are consistent with which of the following
14 of 20
HCM -SCD (Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy – Sudden Cardiac Death) risk scores are used to calculate SCD risk in HCM patients. Which of the following echo parameters are used as part of the scoring system:
15 of 20
Restrictive cardiomyopathy and Constrictive pericarditis may be distinguished based on the following:
16 of 20
PW Doppler interrogation of mitral valve inflow is shown below. E/A ratio is consistent with which grade(s) of diastolic dysfunction:
17 of 20
Mitral inflow and mitral TDI data are shown below 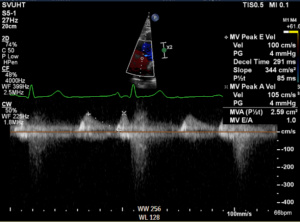
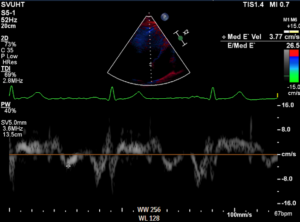
Findings are suggestive of:
18 of 20
PW Doppler interrogation of pulmonary venous flow is shown below. Assuming duration of mitral inflow A wave (Adur) is 105msec, findings are suggestive of
19 of 20
Echo sweep speed for assessment of respiratory variation in mitral and tricuspid valve inflow is best described by
20 of 20
Aortic valve morphology in PSAX aortic valve level is shown below
Findings are consistent with which of the following